API RP 755: The Why, What, and How of This Fatigue Standard

Why Was API RP 755 Created?
If you think safety program management is expensive for an oil and gas company, an accident involving employees and others can be even more costly to the company long term. In petroleum industries in particular, having clear safety rules and regulations for the workplace can be a matter of life and death.
On March 23, 2005, the BP Texas City refinery experienced explosions and fires that resulted in 15 deaths, 180 injuries, and billions of dollars in economic loss. A 2-year investigation from the Chemical Safety Board (CSB) identified several technical and organizational deficiencies – among them was the finding that the operators had been working 12-hour shifts for as many as 29 consecutive days.
In response to this important finding, the American Petroleum Institute (API) created Recommended Practice 755 (RP 755): Fatigue Risk Management Systems for Personnel in the Refining and Petrochemical Industries. The purpose of API RP 755 was to introduce “fatigue prevention guidelines for the refining and petrochemical industries that, at a minimum, limit hours and days of work and address shift work.” This was a necessary first step to establishing industry-wide awareness about the risks posed by fatigue in the workplace.
Which Industries Are Affected?
API RP 755 applies to refineries, petrochemical and chemical operations, natural gas liquids extraction plants, and other facilities such as those covered by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Process Safety Management Standard, 29 CFR 1910.119.
Which Workers Are Affected?
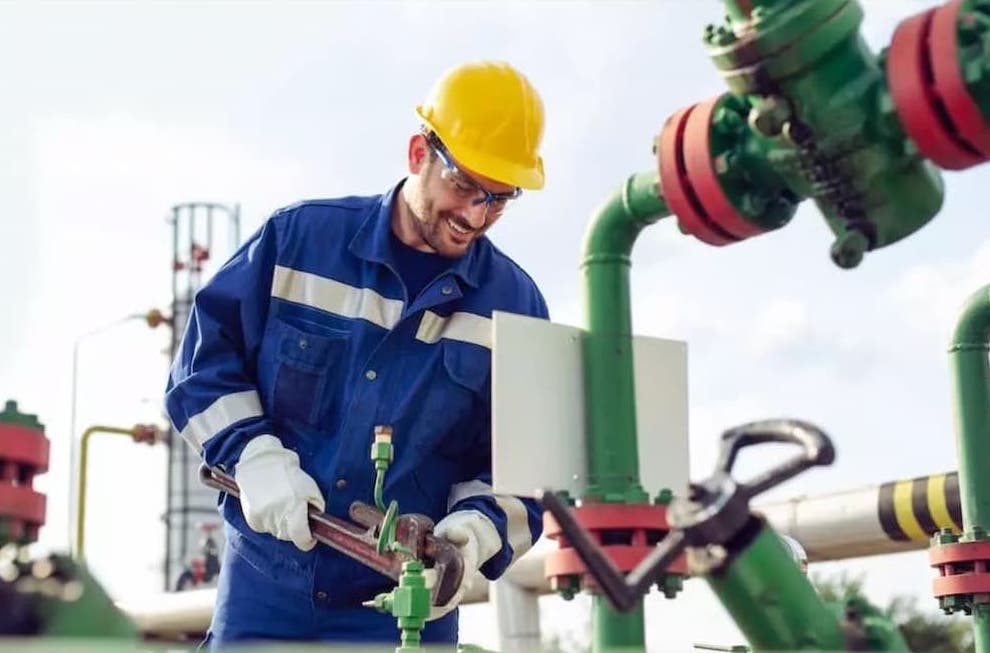
Safety guidelines apply to employees and contractors who perform process safety-sensitive actions during night shifts, rotating shifts, extended hours/days, or call-outs. Safety guidelines also apply to managers and supervisors who make process and safety-sensitive decisions.
What Is Fatigue Risk Management?

Everyone experiences fatigue. A bad night’s sleep can have immediate effects on our mood, reasoning abilities, and even physical appearance. However, prolonged sleep deprivation can have serious consequences for our health, including an increased likelihood of developing cancer and heart disease.
Shift work can cause additional fatigue. Even though risk is a common part of everyday life, many 24/7 operations observe a higher frequency of overtime and extended work shifts which amplifies the potential for hazards. At its best, excessive fatigue can lead to decreased performance and worker dissatisfaction. At its worst, it can result in an injury or a fatal accident.
Addressing fatigue in the workplace requires a comprehensive approach that integrates scientific and medical knowledge with a practical understanding of operational issues.
Several studies have found that tired and sleepy workers are 70 percent more likely to be involved in accidents than well-rested individuals.
A Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS), as described in API RP 755, refers to a comprehensive framework for addressing the risks that may arise from fatigue. Instead of reactionary measures, it emphasizes the optimization of workplace safety at all levels of an organization, before an incident occurs. It encompasses the training and education of employees, in addition to outlining successful management strategies for supervisors.
Fatigue management is a shared responsibility between the managers and the employees. While risk cannot be eliminated, having a scientifically sound, cooperative, fully implemented, and continuously improved FRMS is a necessary first step. Shell Oil, using a robust employee scheduling solution, became the first major oil company to gain full compliance with API RP 755 guidelines across all of its U.S. refineries.
Why Should You Care?
While it is hard to quantify the impact of employee fatigue on a company’s bottom line, the high cost of ignoring the issue is undeniable. When making investment decisions regarding fatigue risk management initiatives, it is essential to consider the many ways employee fatigue can impact workplace operations:
- Overall well-being of employees
- Health benefit costs resulting from job-related injuries
- Productivity losses due to accidents, facility damages, and worker burnout
- Potential for litigations and complaints
- Employment perceptions of highly skilled labor recruits
How Can an Employee Scheduling Solution Mitigate Risk?
A core component of API RP 755 is its Hours of Service guidelines, which provides employee scheduling rules for the maximum number of shifts to be scheduled per employee, and the maximum length of each scheduled shift. It also provides guidance about the minimum rest time required between work sets for each shift pattern, including 12-hour, 10-hour, and 8-hour shifts.
Compliance with these complex rules using a manual scheduling process such as Excel can be a time-consuming and error-prone task. The variance in rules for outages can add to the complexity of managing hundreds or perhaps thousands of employees. An inefficient scheduling practice can lead to severe losses in productivity, compliance violation or in the worst case, an accident that could have easily been avoided.
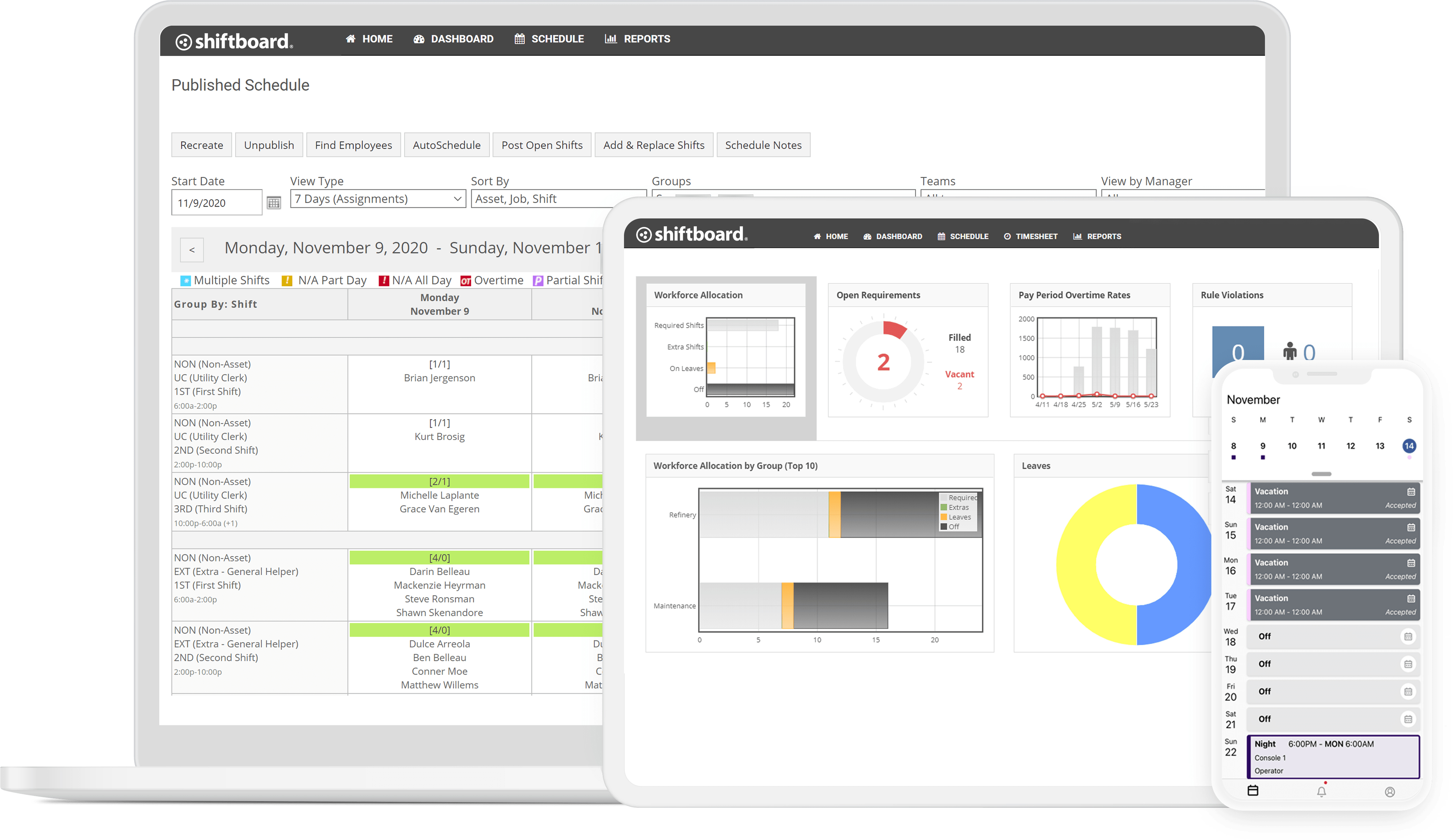
By using a staff scheduling solution that can adapt to all your different industry rules and guidelines, you can simplify and save precious management time, while ensuring your organization is API RP 755 compliant. Solutions such as Shiftboard is an easy-to-use software that is designed to help detect, mitigate and address scheduling issues based on API RP 755, as well as other government, industry and union regulations.
Shiftboard Benefits + Features
- Built-in API RP 755 rules library (editions 1 and 2)
- Continuous monitoring and enforcement of schedule compliance against API RP 755 rules
- Easy-to-understand explanation of rule deviations and schedule action impact
- Audit reports about rules deviation, rule overrides and justifications
Shiftboard and Compliant Workforce Scheduling
In addition to API RP 755, leading enterprises such as Shell, BASF, and INEOS rely on Shiftboard’s solution to ensure workforce scheduling compliance in the following areas:
- Pipeline and Hazardous Materials and Safety Administration (PHMSA) CFR 49 192 and 195
- Labor laws
- OSHA regulations
- Collective bargaining agreements/union agreements
- Federal/state/local regulations
- Internal policies relating to Hours of Service, employee assignment order, overtime equalization, and more